A Black Swan In The Ointment
Authored by Michael Lebowitz and Jack Scott via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
“A good person is as rare as a black swan”- Decimus Juvenal
In 2007, Nassim Taleb wrote a bestselling and highly impactful book titled The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable. The book uses the analogy of a black swan to describe negative events that appear to be very rare and occur without warning. Since the book was published, the term black swan has been overused to describe all kinds of events that were predictable to some degree.
Last April, we wrote A Fly in the Ointment, which was one of a few articles that pointed out the risk of higher inflation to the markets and economy. Thinking about inflation in the context of the Corona Virus and the Fed’s aggressive monetary policy, might our fly be a black swan.
Coronavirus
The economic impact of the Coronavirus has been negligible thus far in the U.S., but in a growing list of other countries, the impact is high. In China, cities more populated than New York City are being quarantined. Citizens are being told to stay at home, and schools, factories, and shops are closed. Japan just closed all of its schools for at least a month. Airlines have reduced or suspended flights to these troubled regions.
From an inflation perspective, the impact of these actions will be two-fold.
-
Consumers and businesses will spend less, especially on elastic goods. Elastic goods are products that are easy to forego or replace with another good. Examples are things like movies, coffee at Starbucks, cruises, and other non-necessities. Inelastic goods are indispensable or those with no suitable replacement. Examples are essential medicines, water, and food. Many items fall somewhere between perfectly elastic and perfectly inelastic, and in many cases, the classification is dependent upon the consumer.
-
On the supply side of the inflation equation, production suspensions are leading to shortages of parts and final goods. Companies must either do without them and slow/suspend production or find new and more expensive sources.
We are purposely leaving out the role that the supply of money plays in inflation for now.
With that as a backdrop, we pose the following questions to help you assess how the virus may impact prices.
-
Will producers of elastic goods lower prices if demand falters?
-
If so, will lower prices induce more consumption?
-
Can producers lower the prices of goods if the cost to produce those goods rise?
-
How much margin compression can companies tolerate?
-
Will producers of inelastic goods try to pass on the higher costs of goods, due to supply chain problems, to consumers?
-
Inflationary or deflationary?
We do not have the answers to the questions but make no mistake; inflation related to hampered supply lines could more than offset weakened demand and pose a real inflation risk.
The Fed’s Conundrum
Monetary policy has a direct impact on prices. To quote from our recent article, Jerome Powell & The Fed’s Great Betrayal:
“One of the most pernicious of these issues in our “modern and sophisticated” intellectual age is that of inflation. Most people, when asked to define inflation, would say “rising prices” with no appreciation for the fact that price movements are an effect, not a cause. They are a symptom of monetary circumstances. Inflation defined is, in fact, a disequilibrium between the amount of currency entering an economic system relative to the productive output of that same system.”
For the past decade, the Fed has consistently sought to generate more inflation. They have kept interest rates lower than normal given the tepid economic growth trends. Further, they employed four rounds of QE. QE provides reserves to banks, which increases their ability to create money. Easy money policies, the type we have grown accustomed to, is designed to increase inflation.
On March 3, 2020, the Fed cut interest rates to try to offset the negative economic impact of the Coronavirus. How lower interest rates will cure a disease is a question for another day. Today’s big question is the Fed fueling the embers of inflation with this sudden rate cut?
Enter the Black Swan
What would the Fed need to do if inflation were to rise due to compromised supply lines and overly aggressive Fed actions? If inflation becomes a problem, they would need to do the opposite of what they have been doing, raise interest rates and reduce the assets on their balance sheet (QT).
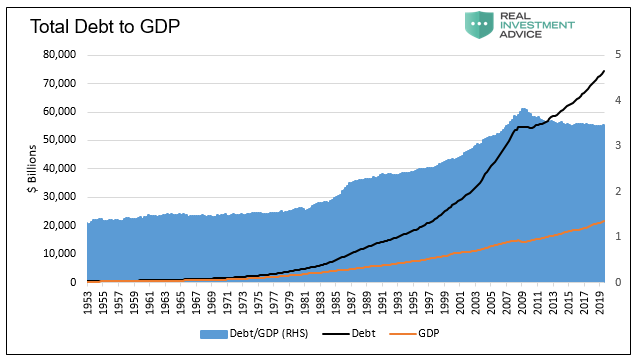
Such policy worked well in the 1970s when Fed Chairman Paul Volker increased Fed Funds to 20% and restricted money supply to bring down double-digit inflation. Today, however, such a prudent policy response would be incredibly problematic due to the massive amount of debt the U.S. and its citizens have accumulated. The graph below shows that there is about three and a half times more debt than annual economic activity currently in the U.S.
Unlike the 1970s, when household, corporate, and public debt levels were much lower, higher interest rates and less liquidity today would inevitably result in massive defaults by both consumers and corporations. Further, it would cause a surge in the Federal budget deficit as interest expense on U.S. Treasury debt would rise.
Over the last few decades, we have seen a steady decline in interest rates. At times in this cycle, rates have risen moderately. Each time this occurred, a crisis developed as funding problems arose. What would happen today if mortgage rates rose to 7% and auto loans to 5%? What would happen to corporate profits if borrowing rates doubled from current levels? How would corporations that depend on routine, cheap refinancing of their debt obtain it?
In such an environment, taking on new debt would be much less appealing and servicing existing debt would require a larger portion of the budget. Clearly, an inflationary outbreak accompanied by higher interest rates would result in a severe recession.
Summary
What is a black swan? A black swan is an unforeseen event like the rapid spreading of the Coronavirus that results in inflation. It is not the obvious outcome but rather an obscure second or third-order effect. Our modern economic policy framework is not designed for inflation, nor are many people even thinking about it as a possibility. That is a black swan.
Inflation is the one thing that prevents the Fed and other central banks from supporting the economy and markets in the way they have become accustomed.
As discussed in prior articles, we believe there is ample evidence of problematic inflation data for those who choose to look. At the same time, global central bankers continue to engage in imprudent policies that are inflationary in nature. Lastly, the Coronavirus threatens to hamper supply lines and change consumer spending habits.
Whether or not those factors result in inflation is unknown. Although one cannot predict the future, one can prepare for it. Inflation is not dead, but it has been hibernating for decades. Even if the odds of inflation are relatively low, that does not mean we should ignore them. As the sub-title to Taleb’s book says, “The Impact of the Highly Improbable” can be important. An event that has a 1% chance of occurring but would cause a massive loss of wealth should not be ignored.
Tyler Durden
Wed, 03/04/2020 – 13:50![]()
Zero Hedge’s mission is to widen the scope of financial, economic and political information available to the professional investing public, to skeptically examine and, where necessary, attack the flaccid institution that financial journalism has become, to liberate oppressed knowledge, to provide analysis uninhibited by political constraint and to facilitate information’s unending quest for freedom. Visit https://www.zerohedge.com